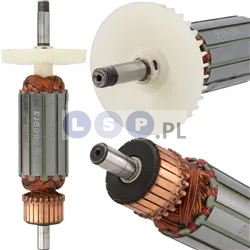
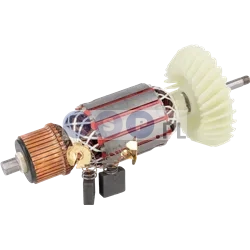
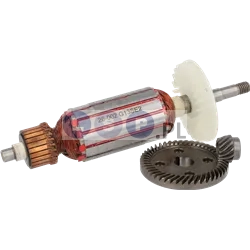
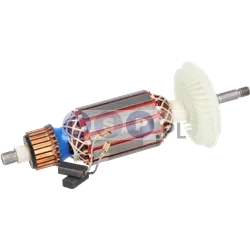
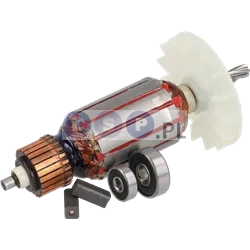
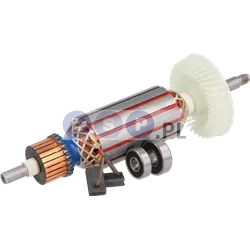
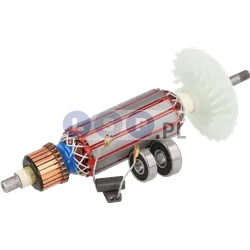
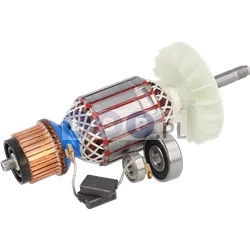
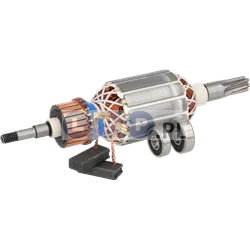
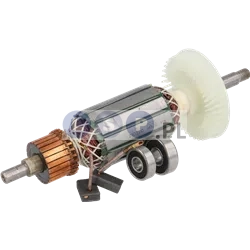
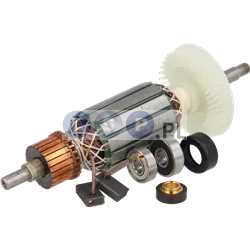
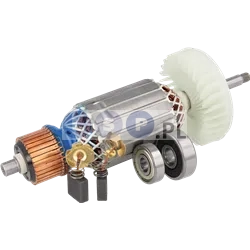
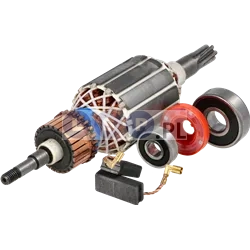
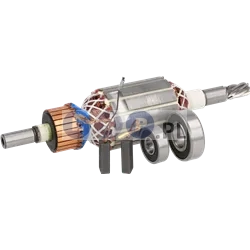
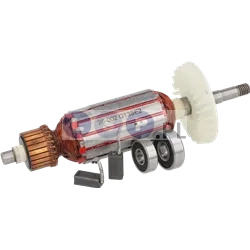
Rotors
Rotors are key components in a variety of power tools, ensuring that they work by generating the rotational motion necessary to perform work such as drilling, cutting or grinding. Our product range includes rotors for: grinders, drills, hammer drills, demolition hammers and other equipment. Reputable brands such as BOSCH, MAKITA, HITACHI, HIKOKI, METABO, DeWALT, HILTI, as well as market, Chinese brands.
How to choose the right rotor?
Each rotor has an original part number for easy selection for branded power tools. For market, Chinese tools, each rotor has dimensions that should be compared with the old part.
Wiatrak wentylator do wirnika GSH 27
zł19.99/ sztukaIndeks: 14-008Średnica Zewnętrzna: 99mm
Średnica Wewnętrzna: 12/15mm (za tuleją)
Grubość: 20mm
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH wiertarka CSB PSB GSB 18-2 20-2
zł69.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-001Wirnik przeznaczony do wiertarki Bosch GSB 18-2 RE. Wirnik pasuje również do: GSB 2-600 RE, GSB 2-650 RE,CSB 650-2 RE, CSB 650-2 RET, CSB 650-2 RP, CSB 6-20 zamiennik: 2 604 010 862, 2 604 011 090 RE, GSB 20-2 RE, GSB 18 RE, GSR 6-20 TE, GSR 8-6 KE, GSB 8-16 KE, CSB 700-2 RE, CSB 680-2 RE.
W magazynieWirnik wiertarki BOSCH GSB 16 RE 2604011077
zł79.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-003Wirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB 16 RE.
Numer katalogowy oryginalny: 2604011077
Wirnik pasuje do elektronarzędzi o numerach:
0 601 140 603
0 601 140 608
0 601 140 637
0 601 140 642
0 601 140 650
0 601 140 670
0 601 140 676 W magazynieWirnik wiertarki BOSCH PSB 450, 2604011173
zł64.80/ sztukaIndeks: 21-004Wirnik do wiertarki Bosch PSB 450. Wirnik pasuje również do: PSB 450-2, PSB 450 RE, PSB 500 RE, PSB 13 RE,PSB 530 RE, PSB 600 RE, PSB 13 RE, PSB 550 RE, PSB 2000.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 2604011173
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Bosch PSB 600 RE 650 2604011154
zł72.45/ sztukaIndeks: 21-006Wirnik do wiertarki PSB 600 RE. Wirnik pasuje również: PSB 600-2, PSB 570 RE, PSB 15 RE, PSB 5-15 RE, PSB 6E, PSB 600 RE, PSB 580 RE, PSB 16 RE, PSB 6-16 RE, SB 600 RPE, PSB 650-2, PSB 650 RE, PSB 650 RPE.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 2604011154
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB13, GSB13RE, 2604011259
zł73.43/ sztukaIndeks: 21-007Wirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB13, GSB13RE.
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 2604011259
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB 20-2 RCE 4 zęby
zł79.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-008Wirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB 20-2 RCE.
Przed zakupem proszę porównać wirnik. Proszę zwrócić szczególną uwagę na kierunek i ilość zębów.
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty produkt.
ZDJĘCIE Z WYMIARAMI MA CHARAKTER POGLĄDOWY.
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB16, GSB16RE, 2604011254
zł82.95/ sztukaIndeks: 21-009Wirnik do wiertarki Bosch GSB16, GSB16RE.
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 2604011254
- 0601148003
- 0601148603
- 0601148608
- 0601148663
- 0601148703
- 0601148708
- 0601148763 W magazynieWirnik Bosch GWS 6-125, 115E, 115, 1604010626
zł49.82/ sztukaIndeks: 21-010Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 6-115, -115E, -125. Wirnik pasuje również do GWS 6-115, GWS 6-125, GWS 660, GWS 6-115 E, GAF 22 A.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1604010626
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki BOSCH GWS850C GWS850CE 8-125
zł50.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-012Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Bosch GWS 850 C.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 604 010 667
Pasuje również do: GWS 850C, GWS 850CE, GWS 780C, GWS 8-100C, GWS 8-125C, GWS 780C, GWS 8-100CE, GWS 8-125CE
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GWS 10-125 C CE PWS 10 HILTI AG
zł89.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-015Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Bosch GWS 10 C. Pasuje również do: GEB 1000 CE, OSB 1020 CE, nowy typ: GWS 10-125 CE, PWS 10-125 CE, HILTI AG 125 S
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 604 010 640
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki BOSCH GWS 1000 GWS 10-125
zł88.90/ sztukaIndeks: 21-016Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 1000.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 604 010 A20
Zastosowanie:
GWS 10-125 Z
GWS 9-125 (0601801008)
GWS 1000
GWS 10-125 /BEZ OZNACZENIA C LUB CE / W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GWS 11-125 CI CIE HILTI DAG DC
zł92.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-017Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 11-125 CI. Wirnik pasuje również do: GWS 11-125 CI, GWS 11-125 CIE, GWS 11-125 CIH. HILTI DAG125SE DAG 125S
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1604010A21
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki typ BOSCH GWS 14 -125 PWS 13
zł82.95/ sztukaIndeks: 21-018Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 14-125 NT.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 604 010 650
Pasuje do:
GBR14CA (601773703)
GWS14-125C (601804503)
GWS14-125C (601704703)
GWS14-125CE (601805708)
GWS14-125CE (601805508)
GWS14-125CE (601705708)
PWS 13-125 CE - pasuje tylko do starego typu bez regulacji obrotów!
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GWS 14-125 CI CIE 1400 1604010A90
zł75.60/ sztukaIndeks: 21-020Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Bosch GWS 14-125 CIE CE.
Szlifierka kątowa: GWS1400, GWS1400C, GWS14-125CI, GWS14-125CIE, GWS 1400, GWS 1400C, GWS 14-125CI, GWS 14-125CIE,
Nr kat.: 1604010A90, 1604010A22, 1604010A86
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki Bosch GWS PWS 20-180 20-230 21-180
zł110.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-021Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 20-230 oraz do PWS 18, 19.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1604011145/1604011148
Wirniki pasuje również: GWS 19-180, GWS 2000-180J, GWS 19-230,GWS 2000-230, GWS 2000-230 J, GWS 21 U, GWS 21-180, GWS 20-230, GWS 21-230, PWS 1700, PWS 20-230, PWS 18-230 J.
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki Bosch GWS 20-230 GWS 21-180 GWS 21-230
zł118.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-022Wirniki pasuje: GWS18U, GWS21U, GWS18-180, GWS19-180, GWS19-230, GWS20-180, GWS20-230, GWS21-180, GWS21-230, GWS2000-230, PWS18-230, PWS19-230, PWS20-230J, PWS 18-230J, GWS 18-180, GWS 19-180, GWS19-230, GWS 20-180, GWS 20-230, GWS 21-180, GWS 21-230, GWS 2000-230, PWS 18-230, PWS 19-230, PWS 20-230J, PWS 18-230J
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1604011148
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki BOSCH GWS 23-230 GWS 24-230
zł124.95/ sztukaIndeks: 21-023Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 23-230. Wirnik pasuje również do: GWS 23-180, GWS 23-230, GWS 24-180, GWS 24-230, GWS 24-300J, GNF 65 A.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1604011153
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki BOSCH PWS 550 600 700 6 7 115 125
zł57.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-024Wirnik pasujący do szlifierek kątowych Bosch PWS 550 . PWS 600 . PWS 650 . PWS 700
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 2609000761
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka Bosch PWS 8-125 9-125 CE
zł68.26/ sztukaIndeks: 21-025Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Bosch PWS 9-125 CE.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 2609000763
Zastosowanie:
GWS 9-125 CS
GWS 9-125 CM
GWS 9-125 CE
GWS 9-150 C
GWS 9-125 C
WS 125 S
GNF 20 CA
R-115
PWS 8-125 CE
PWS 850 CE
PWS EDITION
PWS 9-125 CE
PWS 9-125 X-CEL
PWS 8-125 CE
ORAZ NARZĘDZI SKIL
9280
9285
9290 A1
9290 J1
9295 A1
9295 C1 W magazynieWirnik Bosch GGS 27 C POF 600 ACE GKF 600 CE GGS27
zł79.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-026Wirnik do szlifierki prostej Bosch GGS 27 C POF 600 ACE GKF 600 CE
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 2 604 010 769
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH PBH 160 R PBH 200 180 RE
zł96.39/ sztukaIndeks: 21-027Wirnik do młotowiertarki Bosch PBH 160 R, PBH 160, PBH 200 RE, FRE, PBH 180 RE.
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 1614010144
Last items in stockWirnik Bosch GBH 2-22 GBH 2-23 GBH 2200 1617000524
zł72.45/ sztukaIndeks: 21-029Wirnik do młotowiertarkek Bosch:
GBH 2-22 S , GBH 2-23 RE , GBH 2-22 ,GBH 2-22 RE ,
GBH 2-22 E ,GBH 2-23 S , GBH 2200
Nr. katalogowy: 1617000524
W magazynieWirnik Bosch GBH 2-24DSR 2-24 DFR 5 zębów
zł55.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-030Wirnik do młotowiertarki Bosch GBH 2-24 5 zębów.
W magazynieWirnik GBH2-24DSR GBH2SR GBH2-24DFR 6 ZĘBÓW
zł57.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-031Wirnik do młotowiertarki GBH2-24DSR GBH2SR GBH2-24DFR 6 ZĘBÓW
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1614010227
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GBH2-26 2400 2600 GBH 2-26 DRE
zł58.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-032Wirnik do młotowiertarki Bosch GBH 2-26 DRE.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1614010709 / 1617000560
GBH 2-26 DRE 0 611 253 703 / 708
GBH 2400 3 611 253 803
GBH 2-26 DE 0 611 253 603
GBH 2-26 DFR 0 611 254 703 / 708
GBH 2600 0 611 254 803
GBH 2-26 DBR 0 611 255 503
W magazynieWirnik młot BOSCH GBH 5-38 D GSH 388 GBH5400
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-033Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego GSH 388,GBH 5-38, GBH38. GBH 5400 5-38 500 GSH 500
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1614011083
W magazynieWirnik młot BOSCH GBH 4 DSC GBH 4 DFE
zł74.52/ sztukaIndeks: 21-034Młot Udarowo-Obrotowy GBH 4 DSC, GBH 4 DFE, Numer oryginalny wirnika 1614010128.
WIRNIK DO MASZYNY BEZ ELEKTRONIKI. W PRZYPADKU MŁOTA Z ELEKTRONIKĄ KONIECZNE JEST ODWROTNE PODŁACZENIE DO STOJANA.
PBH 300 E
GBH 4 DSC
DD 540
BBH 4-30 CCE
BHE 4-30 CE
BMH 30-E
GBH 4 DFE
DD 543
GBH 4-TOP
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GBH 5-40DE GBH 5-40DCE GSH 5E 5C
zł149.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-035Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego GBH 5/40DE, GSH 5E. Wirnik przeznaczony jest również do: Młot udarowo-obrotowy: GBH5-40DE, GBH5-40DCE, GSH5E, GSH5CE, GBH 5-40DE, GBH 5-40DCE, GSH 5E, GSH 5CE
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1614011098
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GBH 7DE, 7-45DE, 7-46DE, 1614010213
zł156.45/ sztukaIndeks: 21-037Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego
Młot udarowo-obrotowy: GBH7DE, GBH7-45DE, GBH7-46DE, GBH 7DE, GBH 7-45DE, GBH 7-46DE
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1614010204, 1614010205, 1614010213
W magazynieWirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Bosch GBH 10 DC
zł180.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-038Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Bosch GBH 10 DC.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 617 220 073
W magazynieWirnik młot BOSCH GBH 11 DE GSH 11 E
zł165.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-039Wirnik do młota kruszącego Bosch GSH 11 E, DE.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 614 011 072
W magazynieWirnik młot BOSCH GSH 27, 1614011091
zł205.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-040Wirnik do młota wyburzeniowego Bosch GSH 27.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 614 011 091
W magazynieWirnik pilarki typ BOSCH PKS 54 CE 1604010451
zł105.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-041Wirnik do pilarki Bosch PKS 54, PKS 54 CE.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 1 604 010 451, 1 604 010 314
W magazynieWirnik do pilarki Bosch GKS 55, 65, 1604010328
zł135.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-042Wirnik do pilarki Bosch GKS 55 GSK 65 GKS55 GKS65.
Nr Katalogowy Bosch 1604010328
W magazynieWirnik typ GWS 7-115, GWS 7-125, długi 1619P05210
zł49.90/ sztukaIndeks: 21-043Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 7-125
Odpowiednik oryginału 1619P05210
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GBH2-28 GBH2-28 D DV DFV
zł74.52/ sztukaIndeks: 21-046Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Bosch GBH 2-28 DFV
Nr. katagolowy: 1614010262
GBH 2-28 DV , GBH 2-28 DFV,
GBH 2-28 F , GBH 2-28 , GBH 2-28 D
BHD-2-28 EC
BH 2-28 MES
H 28 MLE POWER
H 28 MLS POWER
W magazynieWirnik typ GWS 12-125 CI CIE 13-125 1607000V33
zł85.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-048Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 12-125, GWS 13-125 CI
Odpowiednik oryginału 1607000V33
Zastosowanie:
GWS 12-125 3 601 G93 000
GWS 12-125 CIE 3 601 G94 000
GWS 12-125 CIEP 3 601 G94 200
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GWS15-125 CI CIE GWS17 1607000V35
zł110.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-049Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 15-125
Odpowiednik oryginału 1607000V35
PASUJE DO MODELI : GWS 15-125 CI , GWS 15-125 CIE ,GWS 15-125 CIP , GWS 15-125 CIPX , GWS 15-125 CIEX , GWS 15-125 CIEP , GWS 17-125 CIE , GWS 17-125 CI , GWS 17-125 CIX , GWS 17- 125 CIEX ,
W magazynieWirnik typ Bosch wiertarka PSB 400 z prosty ząb
zł64.79/ sztukaIndeks: 21-050Wirnik do Wiertarki PSB 400 z prostym zębem
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GBH 2-18 PBH 2000 2100, 1619P01771
zł65.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-051Wirnik do młotowiertarki Bosch PBH 2000 SRE
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 1619P01771
GBH 2-18 RE 3 611 B58 300 / 301
GBH 2-18 RE 3 611 B58 321
PBH 2000 RE 3 603 C44 300
PBH 2000 RE 3 603 CA9 322
PBH 2000 SRE 3 603 C44 301 / 321
PBH 2100 SRE 3 603 CA9 301 / 321
PBH Universal 3 603 CA9 302
PBH 2100 RE 3 603 CA9 320
Last items in stockWirnik szlifierka BOSCH GWS 15 17-125 CIT 1607000V36
zł99.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-052Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej GWS 17-125 CIT
Odpowiednik oryginału 1607000V36
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GSB 16 RE 2604011913
zł78.75/ sztukaIndeks: 21-055Wirnik do wiertarki GSB 16 RE o numerze 2604011913
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki GSB 1600 . GSB 1600 RE, 2609120235
zł54.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-056Wirnik do wiertarki GSB 1600 RE odpowiednik oryginału o numerze katalogowym 2 609 120 235
W magazynieWirnik do pilarki Bosch GKS 190, 1619P06345
zł103.95/ sztukaIndeks: 21-062Wirnik do pilarki GKS 190. Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 1619P06345.
W magazynieWirnik typ BOSCH GWS 9-115 GWS 9-125 GWS 880
zł59.99/ sztukaIndeks: 21-063Wirnik do szlifierek BOSCH GWS 9 oraz 880.
Pasuje do modeli:
GWS 9-115 (3601C96003)
GWS 9-125 (3601C96004, 3601C960022)
GWS 880 (3601C96005, 3601C96006)
GWS 9-115 S (3601C96101, 3601C96103)
GWS 9-125 S (3601C96102, 3601C96104)
GWS 9-125 P (3601C965P1)
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 1619P10952
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GWS 19-125 CI CIE HILTI AG125-19SE 1600A00D2N
zł95.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-064Wirnik szlifierki kątowej Bosch GWX 19-125 S , GWS 19-125 CI , GWS 19-125 CIE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 1600A00D2N.
GWX 19-125 S 3 601 GC8 000
GWS 19-125 CI 3 601 G9N 000
GWS 19-125 CIE 3 601 G9P 000
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GBH 4-32 DFR, BHD SPIT 1614010252
zł124.95/ sztukaIndeks: 21-066Wirnik do młotowieratrki GBH 4-32 DFR. Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 1614010252
numer części:
1614010252
Zastosowanie:
BOSCH
GBH 4-32 DFR
BHD-4-1
BTI-BH 4-32 ME
DD544
SPIT 343
BMH 32-XE
W magazynieWirnik młot Bosch GBH 8-45D DV, GSH 7 VC 1614010267
zł149.00/ sztukaIndeks: 21-067Wirnik do młota GSH 7 VC, GBH 8-45. Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 1614010267
Zastosowanie:
Młot Bosch: GBH8-45DV, GBH8-45D, GSH7VC, GSH9VC,
W magazynieWirnik TYP BOSCH GSH 11 VC 1614011120
zł163.90/ sztukaIndeks: 21-068Wirnik do młota udarowego BOSCH GSH 11 VC (3611C36000)
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 1614011120
W magazynieWirnik do młota GSH 27 VC,1614011139
zł199.80/ sztukaIndeks: 21-069Wirnik do młota GSH 27 VC
numer części: 1614011139
Zastosowanie:
BOSCH
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 0H0
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 0E0
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 090
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 0B0
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 070
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 030
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 040
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 0K0
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 080
- GSH 27 VC - 3 611 C0A 0P0
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki prostej GGS 28 C CE, GGS 28 LC LCE
zł94.40/ sztukaIndeks: 21-070Wirnik do szlifierki prostej GGS 28. Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 3 607 030 476.
GGS 28 C 3 601 B20 000
GGS 28 CE 3 601 B20 100
GGS 28 LC 3 601 B21 000
GGS 28 LCE 3 601 B21 100
W magazynieWirnik TYP BOSCH GBH 2-24 DRE DFR 2400 7 zębów
zł64.90/ sztukaIndeks: 21-072Wirnik do nowej generacji młotków udarowych Bosch GBH 2-24.
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 1619P13450
Pasuje do modeli:
GBH 2-24 DRE / GBH240: 3 611 B72 100, 3 611 B72 180, 3 611 B72 1K0, 3 611 B72 1L1
GBH 2-24 DFR: 3 611 B73 000, 3 611 B73 080, 3 611 B73 0K0, 3 611 B73 0L1
WIRNIK POSIADA 7 ZEBÓW I NIE PASUJE DO MŁOTOWIERTAREK W KTÓRYCH WYSTĘPOWAŁY TWORNIKI Z 6 ZĘBAMI.
W magazynieWirnik typ MAKITA GA 9556 9557 9558 NB HN 515613-9
zł48.99/ sztukaIndeks: 22-003Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita 9556NB 9556HN, 9557NB , 9557HN , 9558NB , 9558HN.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515613-9
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki TYP Makita GA5030, 4530 517649-4
zł45.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-004Wirnik stosowany w szlifierkach:
GA5030, GA4530R, GA5030R, GA4530, PJ7000
Indeks produktu : 22-004
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 517649-4
W magazynieWirnik do MAKITA 9565 CVR 9565CV 9565CR 9565C 515228-2
zł90.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-005Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA.
Wirnik montowany w:
- 9565CV 9565CVR (niektóre typy) 9565CR 9565C
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 515228-2
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty produkt.
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki MAKITA GA9020 GA9020R GA9020S
zł100.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-006Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita GA 9020, MT 900, MT 901, GA7020, GA7020R. GA7020SF
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 517793-7
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA GA 9030 GA 7030R GA 9030R GA 7030S
zł150.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-007Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita GA 9030, GA7030R, GA9030R, GA7030s, GA9030 S.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 517928-4
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki MAKITA GA9040 GA9040R
zł119.70/ sztukaIndeks: 22-008Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita GA 9040.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516958-8, 517833-1
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki GA9049 9047 9057 516708-1
zł145.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-009Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita
9047, 9047 F. 9047 SF. 9049, 9049 F, 9049 SF, 1990
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516708-1
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki MAKITA 9059 SF 9057 516713-8
zł160.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-010Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita
9059 SF
9057
9059
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516713-8
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki Makita 9069 9067 9069 S, 516773-0
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-011Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita 9069/9067.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516773-0
W magazynieWirnik do młotowiertarki HR 2400, 515163-7
zł82.95/ sztukaIndeks: 22-012Wirnik do młotowiertarki HR 2400.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515163-7
W magazynieWirnik do młotka Makita HR2410 HR2420, 517403-6
zł78.74/ sztukaIndeks: 22-013Wirnik do młotowiertarki Makita HR 2410.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 517403-6
W magazynieWirnik TYP MAKITA HR2450 H2440, 515668-4
zł60.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-014Wirnik do wiertarki udarowej z elektroniką Makita HR 2440, 2440X, 2450, 2450T, 2020.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515668-4
W magazynieWirnik wiertarki MAKITA HR2460 HR2470 HR2470F
zł60.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-015Wirnik do wiertarki udarowej z elektroniką HR 2470, HR 2470 F, HR 2470 FT, HR 2470 T, HR 2460 F, HR 2460
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515289-2
W magazynieWirnik typ MAKITA HR4000 HR4040C 516328-1
zł150.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-016Wirnik do młoda udarowego Makita HR 4000C, HR4040C.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516328-1
W magazynieWirnik Makita HR4001C HR4011C HR4010C 513633-7
zł105.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-017Wirnik do młota udarowego Makita HR4001C, HR4011C, HR4010C
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 513633-7
W magazynieWirnik do młota Makita HR4500C, 516843-5
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-018Wirnik do młoda udarowego Makita HR4500C
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516843-5
W magazynieWirnik do młota Makita HR 5001 C, 516778-0
zł160.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-019Wirnik do młoda udarowego Makita HR 5001 C.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516778-0
W magazynieWirnik do młota kującego Makita HM 1100, 515288-7
zł110.25/ sztukaIndeks: 22-020Wirnik do młota kującego Makita HM 1100.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515288-7
W magazynieWirnik do młota MAKITA HM1202, HM1242 C 516803-7
zł135.45/ sztukaIndeks: 22-021Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Makita HM1202C .
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 516803-7T
W magazynieWirnik przecinarki Makita 2414 2412N, 514543-1
zł150.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-022Wirnik przecinarki do metalu Makita 2414.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 514543-1
W magazynieWirnik Makita HP1500, HP1501, HP1510/1600 517108-8
zł61.95/ sztukaIndeks: 22-024Wirnik Makita HP 1500 / HP 1501 / HP 1510 / 1600, 8450 , 8451
Odpowiednik wirnika o numerze: 517108-8
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA HM1304 HM1304B 516864-7
zł165.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-025Wirnik do Wirnik HM1304, Młot kłujący Nr oryginalny 516864-7
W magazynieWirnik młota Makita HM1203C HM1213C HM1205C, 517818-7
zł178.20/ sztukaIndeks: 22-026Wirnik do młota kłujacego HM1203C, HM1213C, HM1205C Numer oryginalny 517818-7
W magazynieWirnik młota MAKITA HR5201, HR5211 516993-6
zł171.72/ sztukaIndeks: 22-027Wirnik do młotowiertarki Makita HR5201, HR5211.
Oryginalny numer 516993-6
W magazynieWirnik typ MAKITA 9554HN 9554NB 9555HN 9555NB
zł44.28/ sztukaIndeks: 22-028Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Makita 9554HN/NB 9555HN/NB.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 515619-7
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka MAKITA GA4540 GA5040 515364-4
zł89.99/ sztukaIndeks: 22-029Wirnik pasuje do szlifierek MAKITA: GA4540 GA5040
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 515364-4
W magazynieWirnik do Makita HR2810 HR2811FT HR2810T HR2810FT, 515294-9
zł72.45/ sztukaIndeks: 22-030Wirnik do młotowiertarki Makita.
Numer oryginalnej części: 515294-9
Element pasuje do modeli: HR2810, HR2811FT, HR2810T, HR2810FT.
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA HR2611FT HR2611F HR2610T HR2600 HR26
zł59.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-031Wirnik do młotowiertarki MAKITA HR2600.
Pasuje również do: HR2611FT HR2611F HR2610T HR26
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 515359-7
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA GA9050 GA7050R GA9050R 518747-7
zł139.32/ sztukaIndeks: 22-032Wirnik do szlifierek MAKITA: GA9050 GA7050R GA9050R
Odpowiednik o numerze oryginału: 518747-7
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA HP2050 HP2051 DP4011 517414-1
zł61.95/ sztukaIndeks: 22-033Wirnik do młotowiertarki MAKITA HP2050.
Pasuje również do: HP2051 DP4011
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 517414-1
W magazynieWirnik typ MAKITA wiertarki HP 1640, 517458-1
zł55.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-034Wirnik do wiertarki udarowej MAKITA HP1640
Pasuje również do: HP1641 HP1640 HP1621 HP1620 HP1641F
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: 517458-1
W magazynieWirnik do młotka MAKITA HR2300 515354-7
zł53.99/ sztukaIndeks: 22-035Wirnik do młotowiertarki HR2300.
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze 515354-7
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej GE 700 W WP WPS 7-125 115 QUICK 310007680
zł79.99/ sztukaIndeks: 23-001Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej
W 7-115 Quick, W 7-125 Quick, WP 7-115 Quick, WP 7-125 Quick,
WPS 7-115 Quick, WPS 7-125 Quick ,W 7-115
Numer części oryginalnej: 310007680
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka METABO W10-150 WQ10-125 QUICK WE14
zł82.95/ sztukaIndeks: 23-003Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Metabo W 10-125, W14
Numery oryginałów: 310007740
PRZED ZAKUPEM PROSZĘ O DEMONTAŻ WIRNIKA I PORÓWNANIE GO WYMIARAMI. ZE WZGLĘDU NA EDYCJE WIRNIKI MIĘDZY SOBĄ MOGĄ SIĘ RÓŻNIĆ.
Nie pasuje do WE 14-125 PLUS z regulacją obrotów
W magazynieWirnik METABO WX 23-230 W2231X WX21180 WX21230
zł156.45/ sztukaIndeks: 23-005Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej WX 23-230 W2231X WX21180 WX212307 W 20-230 21-180 21-230 23-180
PROSZĘ O DEMONTAŻ WIRNIKA ZE SWOJEJ MASZYNY PRZED ZAKUPEM. DO TEGO MODELU MONTOWANE SĄ DWA TYPY WIRNIKÓW. DŁUŻSZY Z TEJ AUKCJI, ORAZ KRÓTSZY, KTÓRY TEŻ JEST WYSTAWIONY.
W magazynieWirnik METABO W WX21-230 W23-180 WX23-230 krótki
zł165.00/ sztukaIndeks: 23-006Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Metabo W 21-180, WX 21-230, W 23-180. WX 23-230, WX2331X, WX21230, W2080
PROSZĘ O DEMONTAŻ WIRNIKA ZE SWOJEJ MASZYNY PRZED ZAKUPEM. DO TEGO MODELU MONTOWANE SĄ DWA TYPY WIRNIKÓW. KRÓTSZY Z TEJ AUKCJI, ORAZ DŁUŻSZY, KTÓRY TEŻ JEST WYSTAWIONY.
Numer oryginalnej części: 310009880
W magazynieWirnik pilarki Black Decker KS805, KS805, BD800, DN800, DN810, KS800, KS810, SR700, 368877-01, 376538-04
zł82.95/ sztukaIndeks: 24-003Wirnik pilarki do cięcia poprzecznego Black Decker KS 805
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 376538-4, 368877-01
Zastosowanie: KS805, KS805, BD800, DN800, DN810, KS800, KS810, SR700
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki prostej Celma PRAa 40, C-33475P
zł86.40/ sztukaIndeks: 25-003Wirnik Celma PRAa 40
Numer katalogowy oryginału: C-33475P W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Celma PRCr10 6S, PRCr10 6ES PRCr10 6AEO, C-33723P
zł45.00/ sztukaIndeks: 25-005Wirnik do wiertarki CELMA
Stosowany w:
- PRCr10 6S, PRCr10 6ES, PRCr10 6 AEO
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: C-33723P
Wirnik mechaniczne bez wad oraz jest fabrycznie nowy.
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty produkt.
W magazynieWirnik wiertarka CELMA PRCb10 PRCb13 aluminiowa
zł75.00/ sztukaIndeks: 25-006Wirnik do wiertarki Celma PRCb 10 13 PRCb10 PRCu PRAa
Numer oryginalnej części: 1119-190-043T
W magazynieWirnik do pilarki Celma DBRCc 67, C-20500/3
zł128.52/ sztukaIndeks: 25-008Wirnik do pilarki Celma DBRCc 67.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: C-20500/3
W magazynieWirnik CELMA PRCj10 LIDER, PRCj10BEO PRCj10CEO C-33871P
zł83.99/ sztukaIndeks: 25-011Wirnik do wiertarki Celma PRCj 10 LIDER,
PRCj 10BEO
PRCj 10CEO
PRCj 10DEO
PRCj 10FEO
Oryginalny numer C-33871P
W magazynieWirnik HITACHI G10SS G11SR2 G12SR2 G13SS 360802E
zł78.74/ sztukaIndeks: 26-001Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Hitachi G10SS, G11SR2, G12SR2, G13SS
Numer oryginału: 360802E
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka Hitachi G13SE2 G12SE2 G13SB3, 360603
zł103.95/ sztukaIndeks: 26-002Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Hitachi G13SE2.
Zastosowanie: Wirnik Hitachi G13SE2, G12SE2, G13SB3, G12SA3 CM5SB SZCZ
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 360-603, 360-603E, 360-619E, 360-734E,
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka HITACHI G18SG G23SE G23SC2 G18SE2 360287E
zł153.36/ sztukaIndeks: 26-003Wirnik do szlifierek kątowych Hitachi G18SG G23SC2 G18SE2 G23SE G23UB
Numer oryginału: 360-287E
W magazynieWirnik Hitachi G23SC3 G23SE2 G18SE3 360594E
zł150.15/ sztukaIndeks: 26-004Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Hitachi G23SC3, G23SE2, G18SE3
G23UB2, G23UA2. G23SE2. G23SC3. G23MRU, G23MR. G18UB2. G18UA2. G18SG2. G18SE3. CM7MC
Numer oryginalnej części: 360-594E
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka Hitachi G23SF2, G18SH, G23U2 360558
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 26-005Wirnik do szlifierek kątowych Hitachi
G18SH2, G18U2, G23SF2, G23U2
Numer oryginału: 360-558
W magazynieWirnik młotka Hitachi DH24PC3 DH24PB3 DH24PM 360720E
zł63.72/ sztukaIndeks: 26-006Wirnik do młotowiertarki Hitachi DH24PB3, DH24PC3, DH24PM
Numer oryginału: 360720E
W magazynieWirnik młota Hitachi DH40MR DH40MRY DH40FR 360591E
zł130.00/ sztukaIndeks: 26-007Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hitachi DH40MR, DH40MRY, DH40FR, DH40SR.
Numer oryginału: 360591E
W magazynieWirnik młota Hitachi H45MR H45MRY H45SR, 360571E
zł131.99/ sztukaIndeks: 26-008Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hitachi H45MR. Wirnik pasuje również do H45MRY H45SR H 45 MR MRY SR.
Numer oryginału: 360571E
W magazynieWirnik młota udarowego Hitachi PH65A 956946E
zł165.00/ sztukaIndeks: 26-009Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego PH 65
Numer oryginału: 956-946E
W magazynieWirnik młotka Hitachi DH24PB2 DH24PC2 360648E
zł74.99/ sztukaIndeks: 26-010Wirnik do młotowiertarki Hitachi DH24PB2
Numer oryginalnej części: 360648E
W magazynieWirnik Hitachi HiKOKI H65SB H65SB2 H70SA 360286E
zł175.00/ sztukaIndeks: 26-011Wirnik do Hitachi H65SB2, H65SB H70 i innych. Odpowiednik oryginału 360286E
W magazynieWirnik młotka HILTI TE 2, TE 2S, TE 2M, 354768-4
zł103.95/ sztukaIndeks: 27-001Wirnik do młotowiertarki Hilti TE 2 TE 2M , TE 2S .
Numer oryginału: 354768-4
WIRNIK PIERWSZEJ GENERACJI. PRZED ZAKUPEM PROSZĘ O DEMONTAŻ WIRNIKA I PORÓWNANIE GO Z TYM, KTÓRY ZAPREZENTOWANY JEST W OFERCIE.
W magazynieWirnik do młotowiertarki Hilti TE 5, 201536
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 27-002Wirnik do młotowiertarki Hilti TE 5
Numer oryginalnej części: 201536
W magazynieWirnik do młota HILTI TE 14 TE 15 TE 18M, 718878-4
zł135.45/ sztukaIndeks: 27-004Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego HILTI TE 14 TE 15 TE 18M.
Numer oryginalnej części: 718878-4
W magazynieWirnik młot udarowy HILTI TE 54 TE 55 TE 504 203263-9
zł142.80/ sztukaIndeks: 27-006Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hilti TE 54, 55, 504, 505.
Numer oryginału: 203263-9
W magazynieWirnik do młota udarowego HILTI TE 72, TE 60, 72343-7
zł160.65/ sztukaIndeks: 27-007Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hilti TE 72.
Numer katalogowy oryginału: 72343-7
W magazynieWirnik do młota Hilti TE 74 TE 75 206250-3
zł146.99/ sztukaIndeks: 27-008Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hilti TE 74, TE 75.
Numer oryginału: 206250-3
W magazynieWirnik do młota udarowego HILTI TE 76 330432-6
zł159.00/ sztukaIndeks: 27-009Wirnik do młota udarowo-obrotowego Hilti TE 76.
Numer oryginału: 330432-6
W magazynieWirnik do młota Hilti TE 24. TE 25, 301144 277155
zł136.00/ sztukaIndeks: 27-012Indeks oryginały: 301144 277155
Zastosowanie: TE 24, TE 25
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki Perles SRE 4-613, SRE 4-613S
zł91.81/ zestawIndeks: 28-003Wirnik do wiertarki Perles SRE 4-613, SRE 4-613S.
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej Perles, Celma HSW 315, HSW 325, HSW 325 CE, HSW 325 RE
zł74.52/ sztukaIndeks: 28-004Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Perles HSW 315, HSW 325, HSW 325 CE, HSW 325 RE.
W magazynieWirnik DeWalt DW 540, 541, BH 40, 41, 577163-04
zł135.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-001Wirnik do młota udarowego DW 540(950W), DW 541(1010W).
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 577163-04
Zastosowanie: BH40, BH41, DW540, DW541, BH 40, BH 41, DW 540, DW 541
W magazynieWirnik DeWALT DW545 DW543 BH45E 571059-00
zł170.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-002Wirnik do młota udarowego DW 545(1100W) oraz BH45E, BH46E, DW543, SH50E, SH50EK, BH 45E, BH 46E, DW 543, DW 545, SH 50E, SH 50EK.
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 571059-00
W magazynieWirnik do DeWALT DW563, DW566, D25002K, D25003K 585289-00
zł150.04/ sztukaIndeks: 29-003Wirnik do Młotowiertarki DW 566 oraz DW563, D25002K, D25003K, BH22, BH24
Numer katalogowy oryginalnej części: 585289-00
W magazynieWirnik DeWALT D28135 D28137 D28136 D28132C
zł107.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-005Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej DeWalt D28132C, D28135, D28136, D28137.
Numer Oryginalny N398000 / 623584-07 .
W magazynieWirnik DeWALT DW501 DW505 DW241 387614-01
zł69.99/ sztukaIndeks: 29-006Wirnik do wiertarki udarowej DeWalt DW241 DW 501 DW 505 DW501 DW505 BM19
Numer oryginalnej części: 387614-01, 387614-00
W magazynieWirnik typ DeWalt D25500, D25600, D25830 580383-02
zł150.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-007Wirnik do DeWalt D25500 typ 1,2, D25600 typ 1,2, D25830 typ 1,2
D25500 typ 1,2,
D25600 typ 1,2,
D25830 typ 1,2
Odpowiednik numerów oryginalnych:
N079385 / 580383-02
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki DeWalt D28414, 28400, 28401, 28410, 28413, 28415, 583530-06 / N029094
zł145.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-008Wirnik do DeWalt D28400, D28401, D28410, D28411, D28413, D28414, D28415
Numer oryginalnej części: 583530-06, N029094
Indeks w sklepe langner-czesci.pl: 29-008
Typ: Zamiennik
W magazynieWirnik DeWALT DWE4050 DWE4051DWE4056 N181765
zł79.90/ sztukaIndeks: 29-009Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej DWE4050 DWE4051
Numer oryginalnej części: N181765
W magazynieWirnik DeWalt DWE4237 DWE4235 DWE4233 N442428
zł77.00/ sztukaIndeks: 29-012Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej marki DeWalt.
Pasuje do modeli: DWE4237 DWE4235 DWE4233
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: N442428
Wykaz modeli:
DWE4237-Type-3
DWE4237-Type-1
DWE4235-Type-3
DWE4233-Type-3
DWE4233-Type-1
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BUŁGAR Eltos-Elprom M-851
zł60.00/ sztukaIndeks: 30-002Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Eltos-Elprom M-851.
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BUŁGAR Eltos-Elprom M-852
zł60.00/ sztukaIndeks: 30-003Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Eltos-Elprom M-852.
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej Eltos-Elprom BUŁGAR MA 2000, MBA 2001
zł140.00/ sztukaIndeks: 30-005Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Eltos-Elprom MA 2000, MBA 2001.
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BUŁGAR Eltos-Elprom MA 2001
zł128.00/ sztukaIndeks: 30-006Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Eltos-Elprom MA 2001
W magazynieWirnik YT 4775, Ferm i inne
zł85.00/ sztukaIndeks: 54-022Wirnik YT 4775, Ferm i inne
W magazynieWirnik REMINGTON 1450
zł68.00/ sztukaIndeks: 54-037Wirnik REMINGTON 1450
Moc 1450 W
W magazynieWirnik do młotowiertarki SDS + - 6 zębów - chińskie marketowe młotowiertarki
zł65.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-002Wirnik do młotowiertarki SDS + - 6 zębów - chińskie marketowe młotowiertarki
W magazynieWiatrak wentylato do GSH388 bez magnesu
zł6.99/ sztukaIndeks: R-079Wentylator do GSH388 bez magnesu
Średnica Zewnętrzna: 79mm
Średnica Wewnętrzna: 15-16.5 (stożek)
Grubość: 17mm
Last items in stockWiatrak wentylator do GSH 5/40 z magnesem
zł16.99/ sztukaIndeks: R-080Wentulator do GSH 5/40 z magnesem
W magazynieKomplet GBH 7 DE - szczotki, łożyska, mimośród
zł279.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-037SLKKomplet GBH 7 DE - szczotki, łożyska, mimośród
Indeks w sklpeie: 21-037SLK
Na komplet składa się: 21-037(wirnik), 46-010(szczotki), NKE628-2RS, 69-072(koło mimośrodowe), 13-014(łożysko igiełkowe)
Numery katalogowe oryginalnych części: 1614010213(wirnik), 1617014135(szczotki), NKE628-2RS(1610900026), 1616317067(koło mimośrodowe), 1610910089(łożysko igiełkowe)
Typ: Zamiennik
Stan: Nowy
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GBH2-24DSR GBH2SR GBH2-24DFR 5 ZĘBÓW
zł72.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-030SWirnik do GBH2-24DSR z 5-cioma zębami wraz ze szczotkami.
Wirnik pasuje jeszcze do amatorskich młotowiertarek GRAPHITE czy EUROTEC.
PRZED ZAKUPEM PROSIMY O DEMONTAŻ WIRNIKA I PORÓWNANIE GO Z OFERTĄ.
W magazynieWirnik do BOSCH GSH11E GBH11E + szczotki
zł169.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-039SWirnik do młota BOSCH GSH GBH 11E wraz ze szczotkami.
W magazynieWIRNIK wiertarka CELMA PRCr 10/6 AEO ES BEO 500W
zł50.00/ zestawIndeks: 25-005SWirnik oraz szczotki węglowe do wiertarki CELMA
Stosowany w:
- PRCr10 6S, PRCr10 6ES, PRCr10 6 AEO
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze: C-33723P
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze szczotki: 1119-110-080
Wirnik mechaniczne bez wad oraz jest fabrycznie nowy.
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty produkt.
W magazynieWirnik SZLIFIERKI GA9050 GA9050R + szczotki
zł129.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-032SWirnik do dużej szlifierki MAKITA GA9050 wraz z wysokiej jakości szczotkami węglowymi.
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki BOSCH GWS11CI CIE HILTI
zł105.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-017SWirnik do szlifierki GWS11CI wraz ze szczotkami.
W magazynieWirnik do BOSCH GWS 7-115 7-125 GEF 7E 1619P05210
zł59.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-043SWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS7 z długim pakietem wraz ze szczotkami wysokiej jakości.
W magazynieWirnik do HITACHI G13SE2 G13SB3 + szczotki
zł130.00/ zestawIndeks: 26-002SWirnik wraz z wysokiej jakości szczotkami węglowymi do szlifierek HITATCHI / HI-KOKIE
W magazynieWirnik do HITACHI G13SE2 G13SB3 PRZEKŁADNIA
zł145.00/ zestawIndeks: 26-002KWirnik wraz z wysokiej jakości przekładnią kątową do szlifierek HITATCHI / HI-KOKI
W magazynieWirnik BOSCH GWS 10-125 C CE PWS 10-125 GWS1000
zł105.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-016SWirnik do szlifierek GWS1000 GWS10 BOSCH wraz ze szczotkami węglowymi.
W magazynieWirnik Bosch GWS 6-115 6-115E GWS6-115 GWS6-115E
zł65.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-010SWirnik do szlifierek kątowych BOSCH GWS6 wraz ze szczotkami wysokiej jakości.
W magazynieWirnik MAKITA 9565CV 9565CR 9565C 9564CV koło
zł105.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-005KWirnik do szlifierek MAKITA z przekładnią kątową.
W magazynieWirnik do podkaszarki kosy wieloklin flora geko black
zł35.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-006Wirnik do podkaszarki kosy wieloklin flora geko black
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki kątowej Flora 230, max G1802-2 i wielu innych
zł108.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-016Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej Flora 230, max G1802-2 i wielu innych
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki mimośrodowej dł.150mm
zł41.51/ sztukaIndeks: 70-026Wirnik do szlifierki mimośrodowej dł.150mm
Last items in stockPordzewiały wirnik do szlifierki Makita 9015 9016 B 516334-6
zł90.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-036RPordzewiały wirnik do szlifierki Makita 9015 9016 B 516334-6
Last items in stockPordzewiały wirnik do polerki geko black einhell 6 zębów
zł75.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-021RPordzewiały wirnik do polerki geko black einhell 6 zębów
W magazyniePordzewiały wirnik do kosy dł. 140mm pak. 38X35mm podkaszarki
zł40.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-022RPordzewiały wirnik do kosy dł. 140mm pak. 38X35mm podkaszarki na wieloklin + łożyska 607ZZ i 608ZZ
W magazyniePordzewiały wirnik Rebir nożyce 6 zębów
zł68.00/ sztukaIndeks: 70-027RPordzewiały wirnik Rebir nożyce 6 zębów
Last items in stockWirnik do wyrzynarki MAKITA 4322 4323 4324 4329 4327 515719-3
zł45.00/ sztukaIndeks: 22-037Wirnik do wyrzynarki MARKI
Stosowany w:
- 4322 4323 4324 4329 4327
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- 515719-3
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty produkt.
W magazynieWirnik szczotki łożyska do wiertarki CELMA PRCr 10/6 AEO ES BEO 500W
zł58.00/ zestawIndeks: 25-005SL-2Zestaw serwisowy do wiertarki CELMA.
Pasuje do:
- PRCr10 6S, PRCr10 6ES, PRCr10 6 AEO
Na sprzedawany komplet składa się:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko 625 RS 2RS wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Łożysko 627 RS 2RS wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Szczotki węglowe komplet; dwie sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: C-33723P
- Szczotki: 1119-110-080
Zdjęcie przedstawia rzeczywisty komplet.
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka MAKITA do szlifierki GA5030 GA4530R GA5030R komplet
zł70.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-004SLA-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GA5030, GA4530R, GA5030R, GA4530, PJ7000
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 517649-4
- Szczotki węglowe: 194722-3, CB459
W magazynieWIRNIK do szlifierki MAKITA 9565CV 9565CVR 9565CR 9565C 9565CV
zł115.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-005SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- 9565CV 9565CR 9565C
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko 6001 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Łożysko 627 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 515228-2
- Szczotki węglowe: 194722-3, CB459
W magazynieWIRNIK do szlifierki MAKITA 9557NB 9558HN 9558NB 9558HNR 9558HNRG
zł75.99/ zestawIndeks: 22-003SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- 9556NB 9556HN, 9557NB, 9557HN, 9558NB, 9558HN
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 515613-9
- Szczotki węglowe: 191978-9 lub 194074-2, CB318, CB325
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS 7-115 GWS 7-125 1619P05210 szczotki
zł65.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-043SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 7-115 GWS 7-125
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko 607 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Łożysko 608 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- AMORTYZATOR
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1619P05210
- Szczotki węglowe: 1619P02870
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki DO BOSCH GWS850CE GWS850C 1 604 010 667 szczotki
zł65.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-012SLA-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 850C, GWS 850CE, GWS 780C, GWS 8-100C, GWS 8-125C, GWS 780C, GWS 8-100CE, GWS 8-125CE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1 604 010 667
- Szczotki węglowe: 2 604 321 005
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki HR2450 515668-4 szczotki łożyska
zł79.99/ zestawIndeks: 22-014SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- MAKITA HR 2440, 2440X, 2450, 2450T, 2020.
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 515668-4
- Szczotki węglowe: 191962-4, CB419
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka BOSCH GWS 14-125 CI CIE 1400 1 604 010 A90 zestaw
zł85.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-020SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS1400, GWS1400C, GWS14-125CI, GWS14-125CIE, GWS 1400, GWS 1400C, GWS 14-125CI, GWS 14-125CIE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1 604 010 A90, 1 604 010 A22, 1 604 010 A86
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 014 138 bądź 1 607 014 176, 1 607 014 172
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka BOSCH GWS 14-125 CI CIE 1400 1 604 010 A90 magnes zestaw
zł95.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-020SLUMWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami, magnesem oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS1400, GWS1400C, GWS14-125CI, GWS14-125CIE, GWS 1400, GWS 1400C, GWS 14-125CI, GWS 14-125CIE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1 604 010 A90, 1 604 010 A22, 1 604 010 A86
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 014 138 bądź 1 607 014 176, 1 607 014 172
- MAGNES ORYGINALNY: 1 607 000 378
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka BOSCH GWS 10-125 C CE PWS 10-125 GWS1000 szczotki
zł89.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-016SLU-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami, magnesem oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 10-125 Z, GWS 9-125 (0601801008) GWS 1000, GWS 10-125 /BEZ OZNACZENIA C LUB CE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1 604 010 A20
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 014 138 bądź 1 607 014 176, 1 607 014 172
W magazynieWIRNIK DO SZLIFIERKI BOSCH GWS 9-115 GWS 9-125 S 1619P10952 ZESTAW
zł75.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-063SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 9-115, GWS 9-125, GWS 9-115 S, GWS 9-125 S, GWS 9-125 P
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1619P10952
- Szczotki węglowe: 1619P11715, 1 619 P11 715, 2 604 321 005, 2604321005, A96
W magazynieWirnik szczotki do szlifierki BOSCH GWS17-125 CI CIE GWS 15-125 1607000V35
zł100.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-049ALS-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 15-125 CI , GWS 15-125 CIE ,GWS 15-125 CIP , GWS 15-125 CIPX , GWS 15-125 CIEX , GWS 15-125 CIEP , GWS 17-125 CIE , GWS 17-125 CI , GWS 17-125 CIX , GWS 17- 125 CIEX
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1607000V35, 1 607 000 V35
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 000 V37 lub 1 607 000 V53
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki DO BOSCH GWS 15-125 CIT GWS 17-125 CIT INOX 1607000V36
zł110.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-052ALS-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 15-125 CIT, GWS 15-150 CI, GWS 15-150 CIP, GWS 17-125 CIT, GWS 17-150 CI, GWS 17-125 INOX, GWS 15-125 INOX
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1607000V36, 1 607 000 V36
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 000 V37 lub 1 607 000 V53
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki MAKITA GA9020 GA9020R GA9020S ŁOŻYSKA SZCZOTKI
zł120.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-006SLWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GA 9020, MT 900, MT 901, GA7020, GA7020R. GA7020SF
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 517793-7
- Szczotki węglowe: CB203, CB204, 191957-7 / 191953-5
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki GBH 2-26 DRE DFR 226 ŁOŻYSKA SZCZOTKI ZESTAW
zł70.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-032SLWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GBH 2-26, GBH 2-26 DRE, GBH 2-26 DE, GBH 2-26 DFR, GBH 2400, GBH 2600
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614010709 / 1617000560, 1 614 010 709 / 1 617 000 560
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 617 000 525
W magazynieWirnik szczotki do BOSCH GWS17-125 CI CIE GWS 15-125 MAGNES KPL
zł115.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-049ALM-2Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami, magnesem oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GWS 15-125, GWS 17-125
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1607000V35, 1 607 000 V35
- Szczotki węglowe: 1 607 000 V37 lub 1 607 000 V53
- ORYGINALNY MAGNES : 1 607 000 v38, 1607000V38
W magazynieWIRNIK szlifierka MAKITA GA9050R GA9050 GA7050R szczotki łożyska
zł158.90/ zestawIndeks: 22-032SL-1Wirnik do szlifierki kątowej MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GA9050 GA7050R GA9050R
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 518747-7
- Szczotki węglowe: 191957-7 / 191953-5, CB203 CB204
W magazynieWirnik 9557 9558 MAKITA SZLIFIERKA KĄTOWA
zł74.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-003KKWirnik w komplecie z przekładnią kątową do szlifierek MAKITA 9558.
W magazynieWirnik GBH2-24DSR GBH2SR GBH2-24DFR SZCZOTKI ŁOŻYSKA
zł75.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-031SLLWirnik do szlifierki kątowej BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami, amortyzatorem oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik montowany w:
- GBH2-24DSR GBH2SR GBH2-24DFR 6 ZĘBÓW
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614010227, 1 614 010 227
- Szczotki węglowe: 1617014134 lub 1617014127, A96, 1 617 014 134 lub 1 617 014 127, A 96
W magazynieWirnik do młotka BOSCH GBH 5-40 DCE 5-40 DE 1614011098 GSH 5E GSH 5CE
zł179.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-035SL-2Wirnik do młota BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GBH5-40DE, GBH5-40DCE, GSH5E, GSH5CE, GBH 5-40DE, GBH 5-40DCE, GSH 5E, GSH 5CE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614011098
- Szczotki węglowe: 1617014135
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki Bosch GWS PWS 20-180 20-230 21-180
zł150.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-021SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 19-180, GWS 2000-180J, GWS 19-230,GWS 2000-230, GWS 2000-230 J, GWS 21 U, GWS 21-180, GWS 20-230, GWS 21-230, PWS 1700, PWS 20-230, PWS 18-230 J.
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604011145/1604011148
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014130 lub 1607014171
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki Bosch GWS PWS 20-180 20-230 21-180 1700 duże szlifierki
zł155.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-022SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS18U, GWS 21U, GWS 18-180, GWS 19-180, GWS 19-230, GWS 20-180, GWS 20-230, GWS 21-180, GWS 21-230, GWS2000-230, PWS18-230, PWS 19-230, PWS 20-230J, PWS 18-230J, GWS 18-180, GWS 19-180
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604011148
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014130 lub 1607014171
W magazynieWirnik do młota BOSCH GSH11E GSH 11 E GBH11DE 1614011072
zł199.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-039SL-2Wirnik do młotka BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko igiełkowe
- Łożysko 6200 ZZ 2ZZ C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614011072
- Szczotki węglowe:1617014126
- Łożysko igiełkowe: 1610910089
➡️Wirnik pasuje do:
- GSH 11 E, GBH 11 DE
W magazynieWirnik do młota BOSCH GSH11E GSH 11 E 1614011072 SZCZOTKI ŁOŻYSKA
zł299.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-039SLKWirnik do młotka BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko igiełkowe
- Łożysko 6200 ZZ 2ZZ C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Koło mimośrodowe
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
➡️Wirnik pasuje do:
- GSH 11 E
W magazynieWirnik do Makita HR4001C HR4011C HR4010C 513633-7 ZESTAW
zł140.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-017SLWirnik do młotka MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko 608 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Łożysko 6201 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 513633-7
- Szczotki węglowe: CB-350, 194160-9
➡️Wirnik pasuje do:
- HR 4001 C, HR 4010 C, HR 4011 C
W magazynieWirnik do DeWalt D28135 D28136 D28137 D28132C zestaw
zł120.00/ zestawIndeks: 29-005SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki DeWALT w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
W zestawie:
- Wirnik
- Łożysko 607 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Łożysko 608 RS 2RS C3 wysokoobrotowe PREMIUM
- Szczotki węglowe z bezpiecznikami komplet; 2 sztuki
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: N398000 / 623584-07
- Szczotki węglowe: 1003860-00 lub 636128-03
W magazynieWIRNIK DO BOSCH GWS 11-125 CI CIE CIH 1 604 010 A21 zestaw
zł105.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-017SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 11-125 CI, GWS 11-125 CIE, GWS 11-125 CIH. HILTI DAG125SE, DAG 125S
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604010A21
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014138, 1607014176, 1607014172, A77
W magazynieWIRNIK DO BOSCH GWS 11-125 CI CIE CIH 1 604 010 A21 zestaw
zł130.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-017SLMWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 11-125 CI, GWS 11-125 CIE, GWS 11-125 CIH. HILTI DAG125SE, DAG 125S
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604010A21
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014138, 1607014176, 1607014172
- Magnes oryginalny: 1607000378
W magazynieWirnik szlifierka BOSCH PWS 550 600 700 6 7 115 2609000761
zł75.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-024SL-2Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- PWS 550, PWS 600, PWS 650, PWS 700, PWS 6-115, PWS 7-115, PWS 720-115
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 2609000761
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014116
W magazynieWIRNIK do wiertarki HITACHI HIKOKI DH24PC3 DH24PB3 ZESTAW
zł95.00/ zestawIndeks: 26-006SLWirnik do wiertarki HITACHI HIKOKI w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
DH24PB3, DH24PC3, DH26PB
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 360720E
- Szczotki węglowe: 999-041
W magazynie-
Wirnik do MAKITA GA9040R GA9040 GA7040 szczotki łożyska
zł165.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-008SLWirnik do szlifierki MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GA7040S, GA7040SF, GA7040R, GA9040R, GA9040S
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 516958-8, 517833-1
- Szczotki węglowe: CB203, CB204, 191957-7, 191953-5
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki MAKITA HP1620 H1621 HP1640 szczotki łożyska
zł90.00/ zestawIndeks: 22-034SLWirnik do wiertarki MAKITA w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- HP1641 HP1640 HP1621 HP1620 HP1641F
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 517458-1
- Szczotki węglowe: 191962-4, CB419, CB-419
W magazynieWirnik do wiertarki BOSCH GBH 2-28F 2-28 DV 2-28 DFV komplet
zł98.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-046SLWirnik do młotowiertarki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
GBH 2-28 DV, GBH 2-28 DFV, GBH 2-28 F, GBH 2-28, GBH 2-28 D, BHD-2-28 EC, BH 2-28 MES, H 28 MLE POWER, H 28 MLS POWER
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614010262
- Szczotki węglowe: 1617000525
W magazynie-
Wirnik BOSCH GBH 7 DE 7-45 DE 7-46 DE 1614010213 ZESTAW
zł195.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-037SLWirnik do MŁOTKA BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GBH7DE, GBH7-45DE, GBH7-46DE, GBH 7DE, GBH 7-45DE, GBH 7-46DE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1614010204, 1614010205, 1614010213
- Szczotki węglowe: 1617014135 zamienne z 1617014144, A69
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS 10-125 C CE GWS 1000 PWS 10 HILTI AG ZESTAW
zł95.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-015SLWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 10 C. GEB 1000 CE, OSB 1020 CE, nowy typ: GWS 10-125 CE, PWS 10-125 CE, HILTI AG 125 S, GWS 1000
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604010640
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014138, 1607014176, 1607014172, A77
W magazynieWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS 14-125 C CE PWS 13-125 CE zestaw
zł95.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-018SLWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 14-125 C, GWS 14-125 CE, PWS 13-125 CE(bez regulacji obrotów)
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604010650
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014138, 1607014176, 1607014172, A77
W magazynieWirnik DO szlifierki BOSCH GWS 23-230 GWS 24-230 szczotki łożyska
zł165.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-023SLWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
- GWS 23-230. GWS 23-180, GWS 23-230, GWS 24-180, GWS 24-230, GWS 24-300J, GNF 65 A.
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1604011153
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607014130, 1607014171, 1619P10476
W magazynieWirnik szlifierki DO BOSCH GWS12-125 CI CIE GWS13-125 CI CIE zestaw
zł110.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-048SLWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
GWS 12-125, GWS 12-125 CIE, GWS 12-125 CIEP
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1607000V33
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607000V37, 1607000V53, 1604321187, HILTI 341529
W magazynie-
Wirnik szlifierki DO BOSCH GWS12-125 CI CIE GWS13-125 CI CIE magnes
zł125.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-048SLMWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
GWS 12-125, GWS 12-125 CIE, GWS 12-125 CIEP
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1607000V33
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607000V37, 1607000V53, 1604321187, HILTI 341529
Magnes, łożyska oryginalne: 1607000V38
W magazynie-
Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS 19-125 CI CIE HILTI AG125-19SE 1600A00D2N
zł125.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-064SLWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
GWX 19-125, GWS 19-125 CI 3 601 G9N 000, GWS 19-125 CIE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1600A00D2N
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607000V37, 1607000V53, 1604321187, HILTI 341529
W magazynie-
Wirnik do szlifierki BOSCH GWS 19-125 CI CIE HILTI AG125-19SE ZESTAW
zł150.00/ zestawIndeks: 21-064SLMWirnik do szlifierki BOSCH w komplecie z łożyskami oraz szczotkami.
➡️Wirnik stosowany w modelach:
-
GWX 19-125, GWS 19-125 CI 3 601 G9N 000, GWS 19-125 CIE
Odpowiednik oryginału o numerze:
- Wirnik: 1600A00D2N
- Szczotki węglowe: 1607000V37, 1607000V53, 1604321187, HILTI 341529
Magnes, łożyska oryginalne: 1607000V38
W magazynie-
29-008SL-2 29-008SL Zestaw D28414 Szczotki, Łożysk
zł145.00/ zestawIndeks: 29-008SL-2 W magazynie
What is a rotor?
The rotor for power tools, is a key component inside many electrical devices such as:
- drills
- angle grinders
- demolition hammers
- hammer
- drills
- screwdrivers
It is the rotating component of an alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) electric motor. It is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
How is the rotor constructed?
- Magnetic core: It consists of a set of laminated steel sheets that form a cylinder.
- The lamination reduces energy losses due to eddy currents.
- Winding
- :
- A copper winding is wound on the core.
- The current flowing through this winding creates a magnetic field.
- Commutator (in DC motors): Located at one end of the rotor and consists of segments that conduct current to the rotor winding. It works with brushes that supply current to the commutator.
How does the rotor function?
- Magnetic induction: The electric current flowing through the rotor winding creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the stator (the stationary part of the motor).
- Rotational motion: The interaction of the magnetic fields of the rotor and stator causes the rotor to start rotating, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy
- .
Types of motors:
- Direct current (DC) motors:
- The rotors in these motors have commutators and brushes.
- Alternating current (AC) motors: Can be of various types, such as induction or synchronous, and in most cases do not have commutators or brushes.
Maintenance and repair:
- Rotors can wear out due to heavy use, overheating or mechanical damage.
- Typical symptoms of rotor damage include sparking, abnormal sounds or a drop in tool power.
- Repairs may include winding replacement, commutator or bearing replacement. Or even the stator. To extend the life of the rotor, it is recommended to buy good quality carbon brushes.